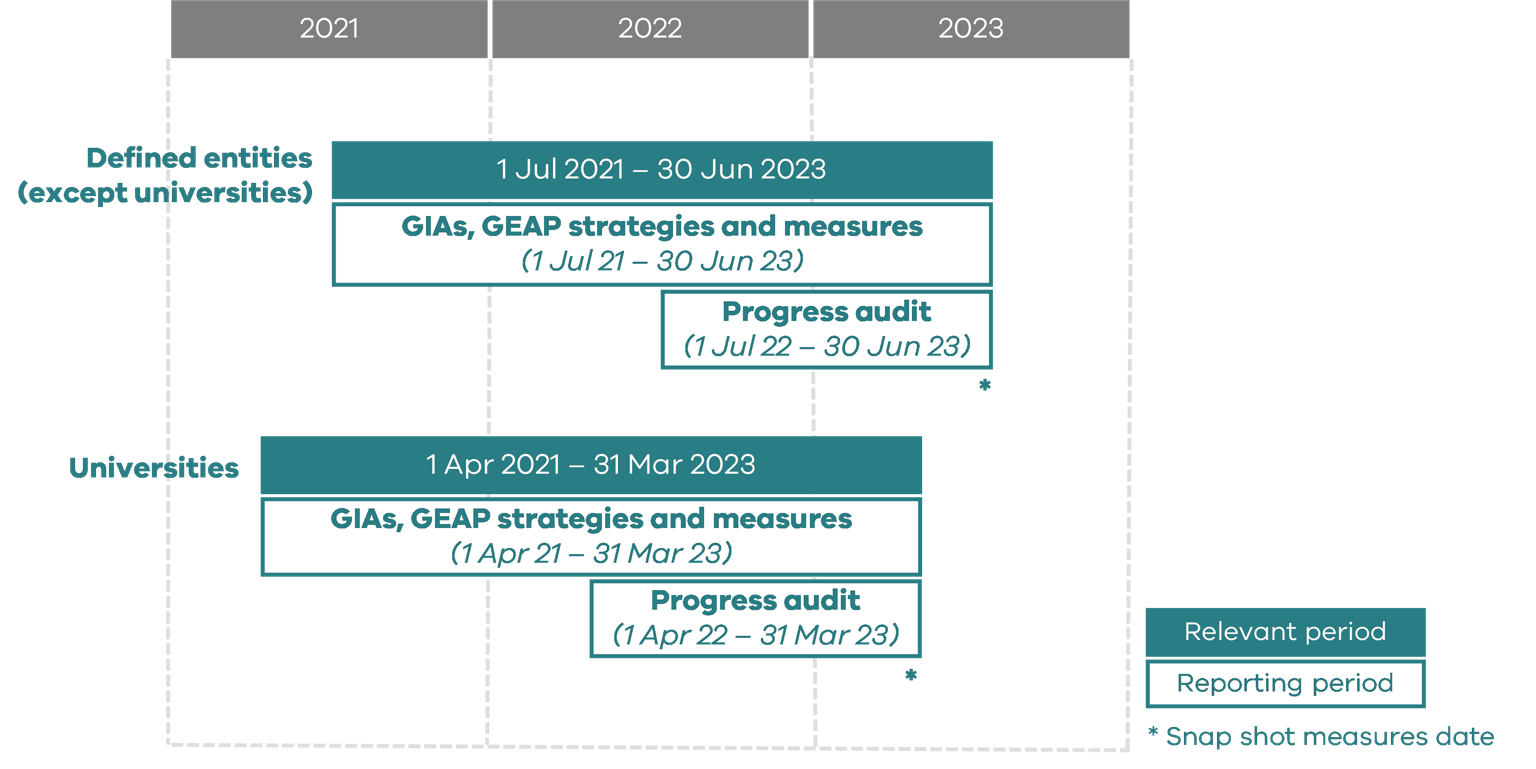
Audit reporting period
The progress audit reporting period is the last 12 months of the relevant period.
For all defined entities except universities, the current audit reporting period is 1 July 2022 to 30 June 2023.
For universities, the current audit reporting period is 1 April 2022 to 31 March 2023, to align with Workplace Gender Equality Agency reporting periods.
Defined entity
The Act applies to certain organisations that have 50 or more employees, including:
- public service bodies
- public entities
- special bodies
- local councils
- universities
- Court Services Victoria
- Office of Public Prosecutions (s5(1))
View our full list of defined entities. Throughout this guidance, defined entities are also referred to as ‘organisations’.
Gender-disaggregated data
Gender-disaggregated data is data that is separated for people of different genders.
Your progress audit should be based on gender-disaggregated data, as this data is critical to assess the progress of gender equality in relation to each of the workplace gender equality indicators.
Gender Equality Action Plan (GEAP)
A Gender Equality Action Plan is a key requirement under the Act which includes strategies and measures that promote gender equality in the workplace of a defined entity, based on the results of a workplace gender audit. Find more information about GEAPs.
Gender pay gap
The gender pay gap is the difference between women’s earnings or people of self-described gender’s earnings and men’s earnings, expressed as a percentage of men’s earnings.
The formula for the gender pay gap is expressed as follows:
A gender pay gap that is positive (greater than 0%) means that men were paid more than women or people of self-described gender. A gender pay gap that is negative (less than 0%) means that women or people of self-described gender were paid more than men.
The reporting platform’s indicator reports will use these formulas to calculate your organisation’s gender pay gap automatically from your employee dataset.
The reporting platform will calculate the gender pay gap based on both mean (average) and median pay.
Intersectional data
Intersectional data (in this context) is data that is separated by gender as well as attributes other than gender, such as Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander identity, age, disability, ethnicity, gender identity, race, religion or sexual orientation.
Looking at data in this way is important. It helps us to understand how someone’s experience of gender inequality might be worsened by the discrimination or disadvantage they may experience based on other attributes.
This concept, referred to in this guide as intersectional gender inequality, recognises that the experiences of an employee who is, for example, an Aboriginal woman, may differ from a non-Aboriginal woman or a woman with disability. Similarly, the experiences of an Aboriginal woman with disability, may differ from a non-Aboriginal woman without disability.
If available, it is recommended that you include intersectional data in relation to the workplace gender equality indicators.
Collecting and analysing this information in your progress audit will help you with preparing your progress report that considers the different systemic barriers that exist in your organisation.
In collecting, analysing and reporting this data, your organisation will need to be sensitive to employee safety, privacy considerations and allow employees the discretion to self-identify attributes. To learn more about intersectional gender inequality and intersectionality, please refer to the leading practice resources page on our website.
Mean
The mean, or average, of a set of values is found by adding all the values and dividing by the total number of values in the set.
Mean remuneration is commonly used in gender pay analysis. It can be skewed by one or a few individuals who have very high or very low salaries, especially for small groups.
Median
The median of a set of values is the middle value when the set is ordered from least to greatest. Half of the set of values are below the median, and half are above the median.
Median remuneration is not used in gender pay analysis as often as mean remuneration, but it can be useful when there are very high or very low salaries in your dataset.
Relevant period
Relevant period means the previous two financial years or other prescribed period prior to the original due date of the progress report. In the case of this progress report, the relevant period is 1 July 2021 to 30 June 2023 (or 1 April 2021 to 31 March 2023 for universities).
Different parts of a progress report will relate to different reporting periods that fall within the relevant period. The progress audit reporting period is the last 12 months of the relevant period.
For all defined entities except universities, the current progress audit reporting period is 1 July 2022 to 30 June 2023.
For universities, the current progress audit reporting period is 1 April 2022 to 31 March 2023, to align with Workplace Gender Equality Agency reporting periods.
Reporting platform
The Gender Equality Act reporting platform (the reporting platform) is how organisations use to submit and view their obligations including Gender Equality Action Plans, audit results and progress reports.
Access to the reporting platform is restricted to registered users.
Updated